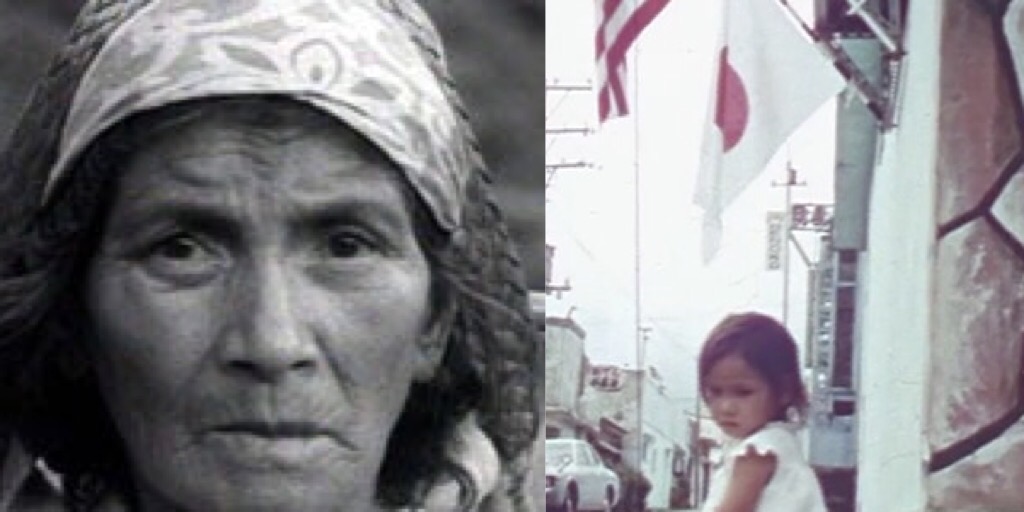
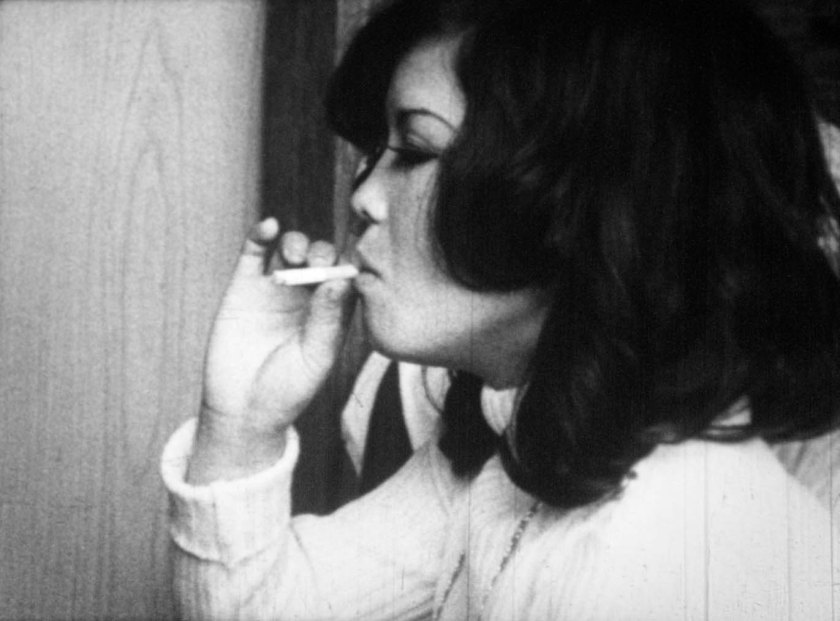
NDU (Nihon Documentary Union) was a Japanese collective established in 1968 by a group of Waseda University students, who would eventually drop out, one of the most prestigious universities in Japan. From 1968 to 1973, the year the group dismantled, this group of activists, they considered themselves first of all as a collective of activists, made four documentaries, moving from the street of Tokyo – the first work was Onikko – A Record of the Struggle of Youth Laborers – to the far away islands in Micronesia passing through Okinawa, the archipelago where they shot two of the their most significant documentaries. Motoshinkakarannu (1971) was made and is about Okinawa before the reversion to Japan, the group went to the island in 1971 and captured on film a society in flux and in the middle of a shifting passage. The film show and focuses on the margins of society with illegal prostitution and life in the red districts, at the same time highlighting the historical and social fractures that were traversing the area: anti-establishment and anti-American riots, the Black Panthers visiting Okinawa, pollution of water and much more. I listed Motoshinkakarannu as one of my favorite Japanese documentaries in the poll I’ve organised a year ago, but today I want to shift my attention on the second movie made by the collective in Okinawa (and beyond): Asia is One (アジアはひとつ), a work that I hadn’t seen at the time of the poll, and that would have certainly figured in my list paired with Motoshinkakarannu.
Asia is One was screened on June 26th at Kyoto Kambaikan, as part of the AAS in Asia, and it was screen with English subtitles for the first time, the movie was shelved for many many years, forgotten, and was (re)discovered only in 2005 when was screened at the Yamagata International Documentary Film Festival. The screening in Kyoto was followed by a fascinating Q&A with the only surviving member of NDU, Inoue Osamu, Nunokawa Tetsurō, who after the dismantling of the collective made other interesting solo documentaries in Palestine and US, passed away in 2012. As described by Roland Domenig (1), with Asia is One
NDU further explored the margins of Okinawan society and continued to break through borders by focusing on the Taiwanese minority. The film portrays Taiwanese migrant workers on the main island of Okinawa who substitute the Okinawa laborers who in turn are employed as migrant workers on Japan’s main islands. It traces the history of Taiwanese coal miners on Iriomote Island, follows legal and illegal workers to the westernmost island of Yonaguni and finally lands in Taiwan in a village of he Atayal tribe of Taiwanese aborigines, where still the Japanese naval anthem is played every noon.
Formally the documentary is composed of landscapes and interviews, all of them out of sync, possibly due to the equipment used or maybe the lack of it. The uncanny space created by this displacement, but also by the use of music from radio broadcasts and kids voices, thrown here and there during the movie, gives the work a peculiar aesthetic tone, a type of non-fiction cinema that I like to call “chaos cinema”. (2)
To explain and understand the “chaotic” trait of Asia is One, and Motoshinkakarannu, we have to delve deeper in the philosophy that laid behind NDU. What the collective has tried to convey through their cinema is extremely fascinating, in their writings (3), mainly published in the magazine Eiga Hihyo, the group was explicitly pushing towards a cinema/activism of anonymity, trying to reach an “impersonal space” and rejecting even the term “work” (sakuhin) because it was seen as the product of a single person in command and as a result of a dominating power structure. In this regard famous was their criticism of Ogawa Production, a collective that bore the name of a single person and that was basically structured hierarchically (4). To this kind of collectivism NDU tried to oppose a more fluid idea of group activism, where the structure was a flat and horizontal one, and in doing so promoting a cinema made by amateurs (5) and not by professionals. “Everybody can push the button and shoot with a 16mm camera” said Inoue, and this is even more true today since the advent of the digital revolution. Whether this approach was successful or not, and more importantly, whether this horizontal structure and “amateur cinema” is possible at all, are questions without answers that are haunting scholars to this day.
Going back to Asia is One, the part of the movie the resonates more with me is the last one, when the film moves to the Atayal village in Taiwan. There’s a quality in the close-ups of the tribe people, beautiful and ancient faces, that is very fascinating, also because it is in these scenes that the political discourse on identity, or the negation of it, reach its peak. From the 17th Century onward The Atayal people, like the rest of the tribes inhabiting the island, had to face the colonization of the Dutch, the Spanish, the Chinese and later of the Japanese (1895 – 1945). Calling them “barbarians” the Japanese Empire tried to assimilate and annihilate their culture (6), the words from the tribe people in the movie add layers of complexity to the situation : “Japan conquered us and abolished many of our ancient traditions and customs”, but at the same time “we were drafted and went to war with pride and ready to die” and “luckily the Japanese abolished some of our ancestral traditions like beheading”.
Asia is One ends with the militaristic song If I Go to Sea against an everyday scene with the aboriginal Taiwanese people isolated in the mountains singing “We want to go to war again.” Of course there is oppression and violence, physical and cultural, in every colonization, but things here are very layered. It seems to me that in this process of cultural and historical coring that the movie conveys, from Okinawa to Taiwan, two very significant points emerge. The first is the crisis of the identity concept, often a forced cultural and national superstructure imposed by the stronger part on a “highly fluid space of human life” (6), as Inoue explained “identity was one of the most hated words inside the NDU, identity is a choking concept”. The second point that struck me is the recurrence of a power and social structure that exploits the margins and the outsiders, in mainland Okinawa the illegal prostitutes and worst jobs are done from people from Miyako island, and in Miyako and other small islands the lower part of society is occupied by Koreans, Taiwanese and aboriginal people.
A final note on the title, the movie as a product of a collective that was thriving towards anonymity, has not film credits, nor it had originally a title, Asia is One was attached to it only later, and it’s a kind of a joke because as Inoue himself said “we all know that Asia is not one!”
notes:
1 Faraway, yet so close by Roland Domenig, in The Legendary Filmmaking Collective NDU and Nunokawa Tetsurō ed. Yasui Yoshio, Tanaka Noriko, Kobe Documentary Film Festival Committee, 2012.
2 This might not be the best way to describe the movie, but aesthetically it reminded me, maybe because of the out of sync, of Imamura Shōhei’s documentaries shot in South East Asia during the 70s.
3 Some of the writings are translated in The Legendary Filmmaking Collective NDU and Nunokawa Tetsurō, op. cit.
4 You can find more in Forest of Pressure: Ogawa Shinsuke and Postwar Japanese Documentary, Abé Markus Nornes, Visible Evidence 2007.
5 Some interesting insights on amateurism in cinema can be found in The Flash of Capital: Film and Geopolitics in Japan,
6 In 1930 the village was the site of an anti-Japanese uprising, the so called Musha Incident, an event portrayed in Warriors of the Rainbow: Seediq Bale (Wei Te-Sheng, 2011)
7 Nunokawa Tetsurō in YIDFF 2005 Special Program, Borders Within – What it means to live in Japan.























You must be logged in to post a comment.